PCB
PCB
Blog Article
Exploring the Evolution and Impact of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
In the intricate world of electronics, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) stand as the backbone upon which our technological marvels are built. These seemingly unassuming boards serve as the foundation for electronic circuits, connecting components and facilitating the flow of electricity with unparalleled precision and efficiency. Let's embark on a journey to unravel the significance, evolution, and impact of PCBs in today's digital landscape. Take a look at the order prototype PCB to learn more.
Understanding PCBs: The Building Blocks of Modern Electronics
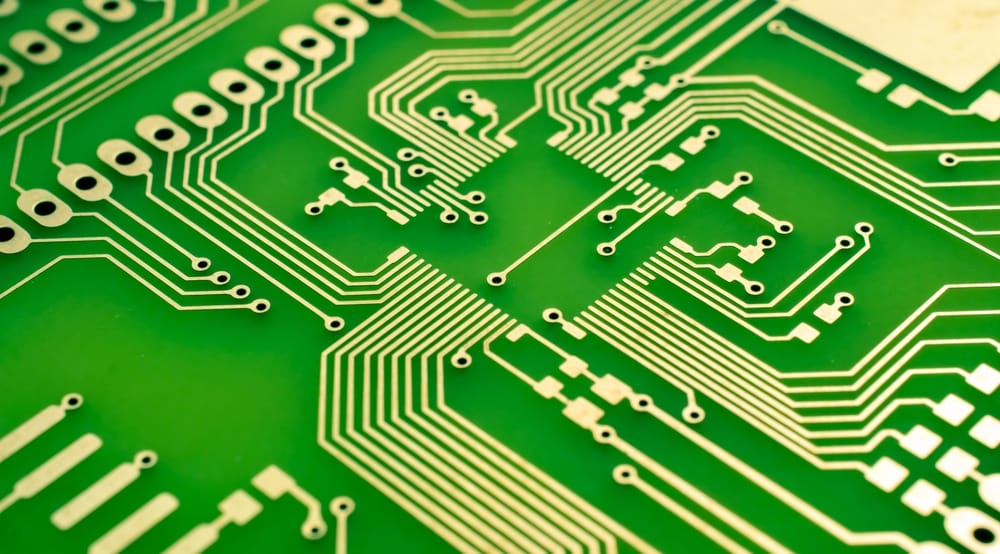
At its essence, a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a flat board composed of a non-conductive substrate, typically fiberglass or composite materials. Copper traces are etched or deposited onto the substrate, forming intricate pathways that interconnect electronic components mounted onto the board. These components encompass a broad spectrum, ranging from basic resistors and capacitors to sophisticated integrated circuits (ICs) and microcontrollers.
The Anatomy of a PCB: Deciphering Its Components
Substrate: The foundational layer of the PCB, providing structural support and electrical insulation.
Copper Traces: Thin conductive pathways etched onto the substrate, serving as channels for electrical signals to flow between components.
Components: Electronic components, such as transistors, diodes, and ICs, are soldered onto the PCB, strategically placed to fulfill specific functions within the circuit.
Solder Mask: A protective layer applied over the copper traces to prevent oxidation and short circuits, enhancing the durability and reliability of the PCB.
Silkscreen: Markings printed onto the PCB's surface, indicating component placement, polarity, and other relevant information for assembly and maintenance purposes.
Unraveling the Functionality of PCBs: How They Work
PCBs serve as the nerve center of electronic devices, orchestrating the seamless transmission of electrical signals between components. When powered on, these signals traverse the copper traces, guided by the circuit's design, to execute a myriad of functions dictated by the device's intended purpose. Whether it's a smartphone, a medical device, or a spacecraft, PCBs play a pivotal role in ensuring the functionality and performance of modern electronics.
The Pervasive Influence of PCBs: Key Advantages and Applications
Miniaturization: PCBs enable the compact integration of electronic components, facilitating the development of smaller, sleeker, and more portable devices.
Reliability: By providing a stable platform for component placement and interconnection, PCBs enhance the reliability and durability of electronic systems, minimizing the risk of failures and malfunctions.
Scalability: PCBs are highly scalable and adaptable, capable of accommodating diverse electronic components and configurations to meet the demands of various industries, including telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
Manufacturability: PCBs can be mass-produced using automated manufacturing processes, ensuring cost-effectiveness, consistency, and scalability in production.
Charting the Future Trajectory of PCB Technology: Emerging Trends and Innovations
High-Density Interconnects (HDI): The evolution of HDI technology enables the fabrication of PCBs with increased routing density and reduced form factors, paving the way for smaller and more powerful electronic devices.
Flexible and Rigid-Flex PCBs: Innovations in flexible and rigid-flex PCBs offer enhanced versatility and durability, enabling applications in wearable electronics, medical implants, and automotive systems.
Advanced Materials: The development of novel materials, such as conductive inks and substrate composites, enhances the performance, reliability, and thermal management capabilities of PCBs in demanding environments.
In Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of PCBs
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) represent the epitome of innovation and engineering prowess in the realm of electronics. From their humble beginnings to their indispensable role in shaping the digital landscape, PCBs continue to push the boundaries of possibility, driving progress and innovation in every facet of modern life. As we embark on the journey towards a more connected and technologically advanced future, the legacy of PCBs will undoubtedly remain etched in the annals of history as a testament to human ingenuity and perseverance.
Report this page